Since the values that a variable takes are usually numerical, a few world should be said about the number system.
Natural Numbers ( ) - Contains all positive number and 0 (0, 1, 2, 3, 4...)
) - Contains all positive number and 0 (0, 1, 2, 3, 4...)
Integers (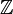 ) - Contains both positive and negative integers. (..., -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, ...)
) - Contains both positive and negative integers. (..., -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, ...)
Rational Number ( ) - Integers, of course, do not exhaust all the possible numbers, for we have fractions, such as 2/3, 4/5, which - if placed on a ruler, would fall between the integers. So any number that can be expressed as a ratio of two integers in called a rational number. But integers themselves are rational, because any integer n can be considered as the ratio n/1. Please note that the characteristic of a rational number is that it is expressible as either a terminating decimal or repeating decimal.
) - Integers, of course, do not exhaust all the possible numbers, for we have fractions, such as 2/3, 4/5, which - if placed on a ruler, would fall between the integers. So any number that can be expressed as a ratio of two integers in called a rational number. But integers themselves are rational, because any integer n can be considered as the ratio n/1. Please note that the characteristic of a rational number is that it is expressible as either a terminating decimal or repeating decimal.
Natural Numbers (
 ) - Contains all positive number and 0 (0, 1, 2, 3, 4...)
) - Contains all positive number and 0 (0, 1, 2, 3, 4...)Integers (
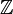 ) - Contains both positive and negative integers. (..., -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, ...)
) - Contains both positive and negative integers. (..., -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, ...)Rational Number (
 ) - Integers, of course, do not exhaust all the possible numbers, for we have fractions, such as 2/3, 4/5, which - if placed on a ruler, would fall between the integers. So any number that can be expressed as a ratio of two integers in called a rational number. But integers themselves are rational, because any integer n can be considered as the ratio n/1. Please note that the characteristic of a rational number is that it is expressible as either a terminating decimal or repeating decimal.
) - Integers, of course, do not exhaust all the possible numbers, for we have fractions, such as 2/3, 4/5, which - if placed on a ruler, would fall between the integers. So any number that can be expressed as a ratio of two integers in called a rational number. But integers themselves are rational, because any integer n can be considered as the ratio n/1. Please note that the characteristic of a rational number is that it is expressible as either a terminating decimal or repeating decimal.
Irrational Number - Cannot be expressed expressed as ratios of a pair of integers (√2, π). Please note that the irrational numbers form non-repeating, non-terminating decimals.
Real Number ( ) - Every real number is either rational or irrational. Every real number corresponds to a point on the number line.
) - Every real number is either rational or irrational. Every real number corresponds to a point on the number line.
 ) - Every real number is either rational or irrational. Every real number corresponds to a point on the number line.
) - Every real number is either rational or irrational. Every real number corresponds to a point on the number line.
Imaginary Number - A multiple of the imaginary unit i (the square root of -1).
Complex Number (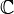 ) - This set of numbers arose, historically, from trying to find closed formulas for the roots of cubic and quartic polynomials. This led to expressions involving the square roots of negative numbers, and eventually to the definition of a new number: the square root of −1, denoted by i, a symbol assigned by Leonhard Euler, and called the imaginary unit. The complex numbers consist of all numbers of the form
) - This set of numbers arose, historically, from trying to find closed formulas for the roots of cubic and quartic polynomials. This led to expressions involving the square roots of negative numbers, and eventually to the definition of a new number: the square root of −1, denoted by i, a symbol assigned by Leonhard Euler, and called the imaginary unit. The complex numbers consist of all numbers of the form
a + bi or
a + ib
where a and b are real numbers. In the expression a + bi, the real number a is called the real part and b is called the imaginary part. If the real part of a complex number is 0, then the number is called an imaginary number or is referred to as purely imaginary; if the imaginary part is 0, then the number is a real number. Thus the real numbers are a subset of the complex numbers. If the real and imaginary parts of a complex number are both integers, then the number is called a Gaussian integer.
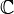 ) - This set of numbers arose, historically, from trying to find closed formulas for the roots of cubic and quartic polynomials. This led to expressions involving the square roots of negative numbers, and eventually to the definition of a new number: the square root of −1, denoted by i, a symbol assigned by Leonhard Euler, and called the imaginary unit. The complex numbers consist of all numbers of the form
) - This set of numbers arose, historically, from trying to find closed formulas for the roots of cubic and quartic polynomials. This led to expressions involving the square roots of negative numbers, and eventually to the definition of a new number: the square root of −1, denoted by i, a symbol assigned by Leonhard Euler, and called the imaginary unit. The complex numbers consist of all numbers of the forma + bi or
a + ib
where a and b are real numbers. In the expression a + bi, the real number a is called the real part and b is called the imaginary part. If the real part of a complex number is 0, then the number is called an imaginary number or is referred to as purely imaginary; if the imaginary part is 0, then the number is a real number. Thus the real numbers are a subset of the complex numbers. If the real and imaginary parts of a complex number are both integers, then the number is called a Gaussian integer.

No comments:
Post a Comment